Titled “Emerging Energy-Efficient Biosignal-Dedicated Circuit Techniques: A Tutorial Brief”, this contribution has been published in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. In this publication, we present a concise overview of emerging energy-efficient biosignal-dedicated circuits from bandwidth- and computation-reduction perspectives. Congratulations to Ph.D. student Shiqi Zhao and to this paper’s co-authors for the excellent achievement.
Citation
S. Zhao, C. Fang, J. Yang, and M. Sawan, “Emerging Energy-Efficient Biosignal-Dedicated Circuit Techniques: A Tutorial Brief”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2022.3169004
Abstract
High spatiotemporal resolution biosignal that is vital for biomedical applications results in an information bottleneck that poses challenges for their transferring and processing. The energy efficiency of biosignal-dedicated circuits becomes increasingly important with the emergence of wearable and implantable healthcare devices where low power consumption must be fulfilled. This tutorial brief presents a concise overview of emerging energy-efficient biosignal-dedicated circuits from bandwidth- and computation-reduction perspectives, aiming to provide designers with a guideline for different design choices.
More information can be found at the following link:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9760507
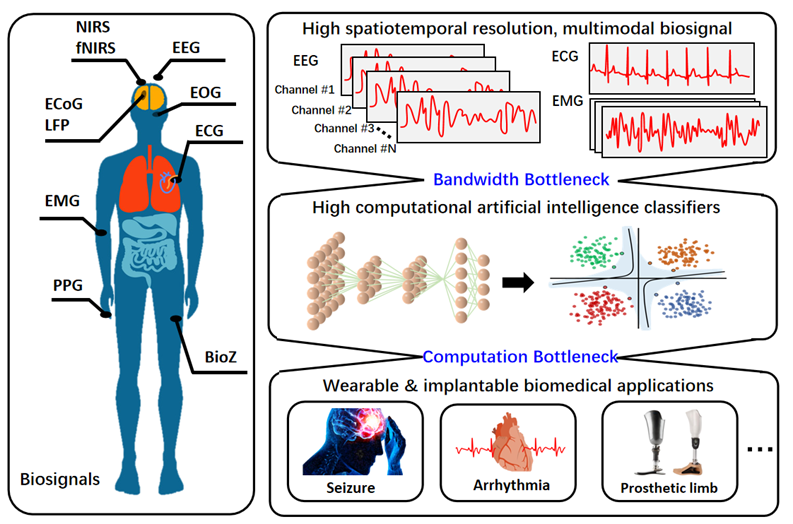
Fig.1: Building blocks of conventional biomedical devices. EEG, EMG, and ECG are among the biosignals used for various applications, including seizure prediction, arrhythmia detection, and gesture recognition.