Titled “On-Site Biolayer Interferometry-Based Biosensing of Carbamazepine in Whole Blood of Epileptic Patients”, this contribution has been published in the Biosensors journal. In this publication, we present two types (being indirect vs. direct) of fiber-optic biolayer interferometry (FO-BLI) biosensors for on-site carbamazepine monitoring. The work proves that Direct FO-BLI is more effective for integration into the clinic by delivering carbamazepine values from whole blood within minutes. Congratulations to Sumin Bian, Research Assistant Professor, and to this paper’s co-authors for this excellent achievement.
Citation
Bian, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, P.;Wang, Q.;Wu, H.; Sawan, M. On-Site Biolayer Interferometry- Based Biosensing of Carbamazepine in Whole Blood of Epileptic Patients. Biosensors 2021, 11, 516.
Abstract
On-site monitoring of carbamazepine (CBZ) that allows rapid, sensitive, automatic, and high-throughput detection directly from whole blood is of urgent demand in current clinical practice for precision medicine. Herein, we developed two types (being indirect vs. direct) of fiber-optic biolayer interferometry (FO-BLI) biosensors for on-site CBZ monitoring. The indirect FO-BLI biosensor preincubated samples with monoclonal antibodies towards CBZ (MA-CBZ), and the mixture competes with immobilized CBZ to bind towards MA-CBZ. The direct FO-BLI biosensor used sample CBZ and CBZ-horseradish peroxidase (CBZ-HRP) conjugate to directly compete for binding with immobilized MA-CBZ, followed by a metal precipitate 3,30-diaminobenzidine to amplify the signals. Indirect FO-BLI detected CBZ within its therapeutic range and was regenerated up to 12 times with negligible baseline drift, but reported results in 25 min. However, Direct FO-BLI achieved CBZ detection in approximately 7.5 min, down to as low as 10 ng/mL, with good accuracy, specificity and negligible matric interference using a high-salt buffer. Validation of Direct FO-BLI using six paired sera and whole blood from epileptic patients showed excellent agreement with ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Being automated and able to achieve high throughput, Direct FO-BLI proved itself to be more effective for integration into the clinic by delivering CBZ values from whole blood within minutes.
More information can be found at the following link:
https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120516
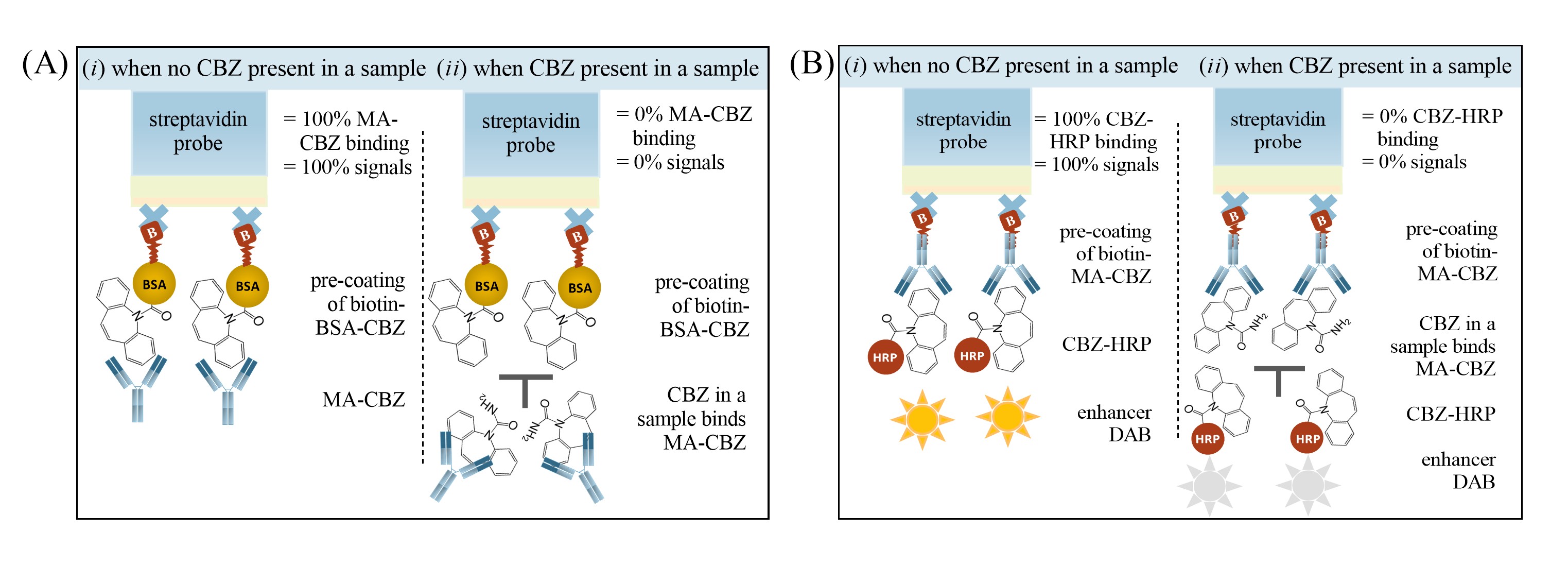 Fig.1: he principle of on-site CBZ monitoring for the (A) indirect FO-BLI biosensor via indirect competitive binding and (B) direct FO-BLI biosensor via direct competitive binding.
Fig.1: he principle of on-site CBZ monitoring for the (A) indirect FO-BLI biosensor via indirect competitive binding and (B) direct FO-BLI biosensor via direct competitive binding.