Depression is a multifactorial disease with unknown etiology affecting globally. It’s the second most significant reason for infirmity in 2020, affecting about 50 million people worldwide, with 80% living in developing nations.
A recent study published in the journal Complex & Intelligent Systems titled "Unravelling the complexities of depression with medical intelligence: exploring the interplay of genetics, hormones, and brain function". This survey delves into the intricate associations between psycho-neurological behaviors like stress and anxiety and depression. It explores changes in various physiological markers during depression, including genes, proteins, hormones, and inflammation.
Notably, it highlights the significant role of medical intelligence in detecting, predicting, and treating depression. The survey also offers insights into current diagnostic and treatment approaches, identifies research gaps, and provides recommendations for future studies.
This comprehensive review aims to guide researchers, doctors, and scholars in understanding and addressing depression from multiple perspectives, including medical, biological, psychological, and engineering aspects.
Congratulations to our postdoctoral fellow Md Belal Bin Heyat and to co-authors for this achievement.
Reference
Heyat, M.B.B., Akhtar, F., Munir, F. et al. Unravelling the complexities of depression with medical intelligence: exploring the interplay of genetics, hormones, and brain function. Complex Intell. Syst. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-024-01346-x
More information can be found at the following link:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40747-024-01346-x#Ack1
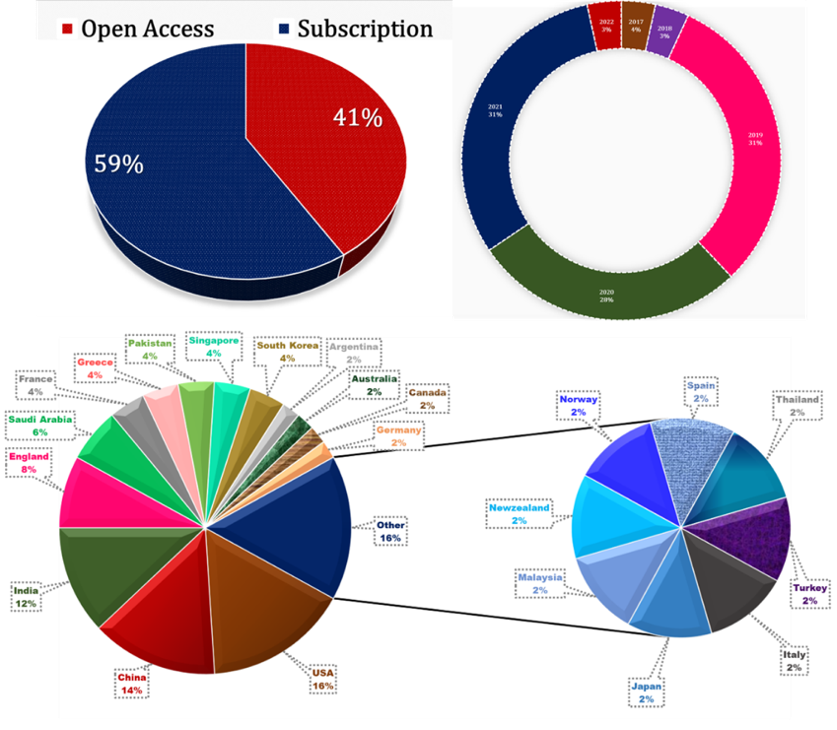
Fig.1: Details for the previously published articles related to depression with machine learning and deep learning.
Research Highlights
Comprehensive Analysis and Methodology: The study covers various facets of depression, from understanding relationships and classifications to identifying and recognizing symptoms, analyzing effects, and exploring detection and treatment methods, utilizing both traditional and emerging technologies. It employs rigorous methodologies and visual representations, including the use of VOSviewer and word clouds to aid comprehension.
Role of AI and Emerging Technologies: It enlightens the potential of artificial intelligence in improving the diagnosis and treatment of depression, summarizing major tools and machine learning methods. The present techniques and suggested advancements in AI can further enhance healthcare research, especially in the context of depression, opening new avenues for utilizing emerging technologies.
Identified Research Gaps and Future Directions: It identifies existing research gaps and provides future directions for readers to explore depression within their research interests, particularly focusing on the application of AI in medical fields.
Interdisciplinary Approach: By integrating multidisciplinary perspectives, the study aims to guide researchers, doctors, and scholars in understanding and addressing depression from medical, biological, psychological, and engineering angles.
Abstract
The main purpose of this study is to determine the volume of depression research conducted on different aspects such as genetics, proteins, hormones, oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and associations with other mental disorders like anxiety and stress using traditional and medical intelligence (medical with AI). In addition, it also designs a comprehensive survey on detection, treatment planning, and genetic predisposition, along with future recommendations. This work is designed through different methods, including a systematic mapping process, literature review, and network visualization.
In addition, we also used VOSviewer software and some authentic databases such as Google Scholar, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science for data collection, analysis, and designing comprehensive picture of the study. We analyzed 60 articles related to medical intelligence, including 47 from machine learning with 513,767 subjects (mean ± SD = 10,931.212 ± 35,624.372) and 13 from deep learning with 37,917 subjects (mean ± SD = 3159.75 ± 6285.57). Additionally, we also found that stressors impact the brain’s cognitive and autonomic functioning, resulting in increased production of catecholamine, decreased cholinergic and glucocorticoid activity, with increased cortisol. These factors lead to chronic inflammation and hinder the brain’s normal functioning, leading to depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular disorders.
In the brain, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production is increased by IL-6 stimulation and mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase is inhibited by nitric oxide, a potent inhibitor. Proteins, lipids, oxidative phosphorylation enzymes, and mtDNA are further disposed to oxidative impairment in the mitochondria. Consequently, mitochondrial dysfunction exacerbates oxidative stress, impairs mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or deletions of mtDNA, increases intracellular Ca2+ levels, changes in fission/fusion and mitochondrial morphology, and lastly leads to neuronal death. This study highlights the multidisciplinary approaches to depression with different aspects using traditional and medical intelligence. It will open a new way for depression research through new emerging technologies.
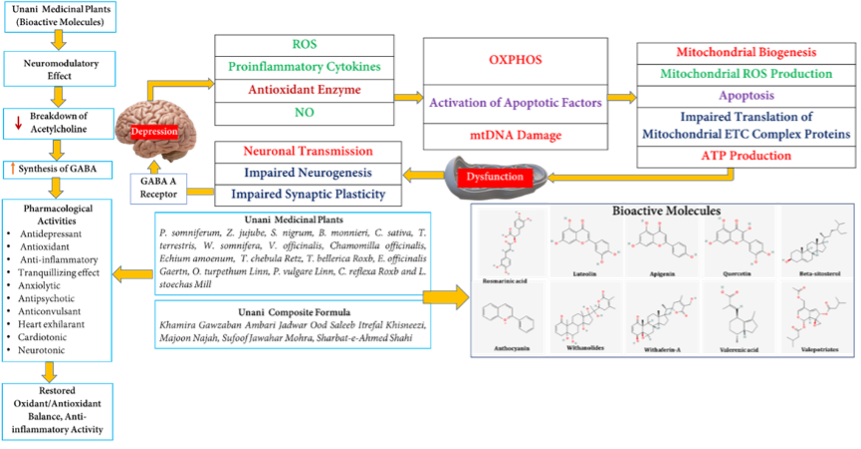
Fig.2: Depiction of the role of oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory process in depression and actions of bioactive molecules of herbal medicines as antidepressant, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory.