Titled “Biosensors for waterborne virus detection: Challenges and strategies”, this contribution has been published in Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. This review suggests that implementing a comprehensive system that integrates the entire waterborne virus detection process with high-accuracy analysis could enhance virus monitoring.
Congratulations to the first author, Xixi Song and to this paper’s co-authors for this excellent achievement.
Reference
Xixi Song, Zina Fredj, Yuqiao Zheng, Hongyong Zhang, Guoguang Rong, Sumin Bian, Mohamad Sawan. Biosensors for waterborne virus detection: Challenges and strategies[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2023, 13(11): 1252-1268.
Abstract
Waterborne viruses that can be harmful to human health pose significant challenges globally, affecting health care systems and the economy. Identifying these waterborne pathogens is essential for preventing diseases and protecting public health. However, handling complex samples such as human and wastewater can be challenging due to their dynamic and complex composition and the ultralow concentration of target analytes. This review presents a comprehensive overview of the latest breakthroughs in waterborne virus biosensors. It begins by highlighting several promising strategies that enhance the sensing performance of optical and electrochemical biosensors in human samples. These strategies include optimizing bioreceptor selection, transduction elements, signal amplification, and integrated sensing systems. Furthermore, the insights gained from biosensing waterborne viruses in human samples are applied to improve biosensing in wastewater, with a particular focus on sampling and sample pretreatment due to the dispersion characteristics of waterborne viruses in wastewater. This review suggests that implementing a comprehensive system that integrates the entire waterborne virus detection process with high-accuracy analysis could enhance virus monitoring. These findings provide valuable insights for improving the effectiveness of waterborne virus detection, which could have significant implications for public health and environmental management.
More information can be found at the following link:
https://jpa.xjtu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.1016/j.jpha.2023.08.020
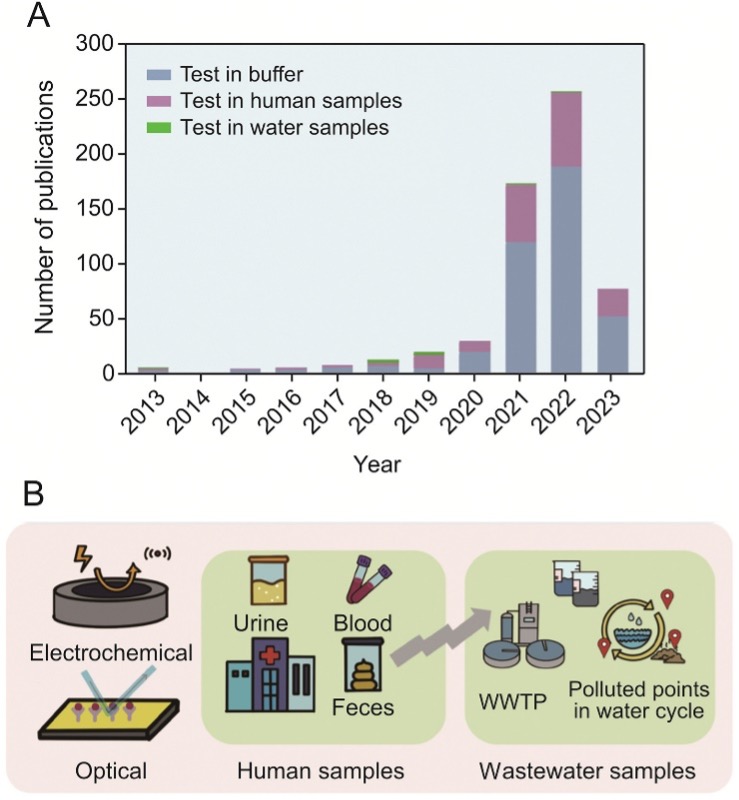
Fig. 1: Trends and evolution in biosensors for waterborne virus detection. (A) Publications regarding biosensors for waterborne virus detection in the past two decades (Web of Science). (B) Developed biosensors (electrochemical, optical) applied in human samples and wastewater samples. The insights gained from the biosensing waterborne viruses in human samples can be adapted to improve biosensing in wastewater. WWTP: wastewater treatment plant.
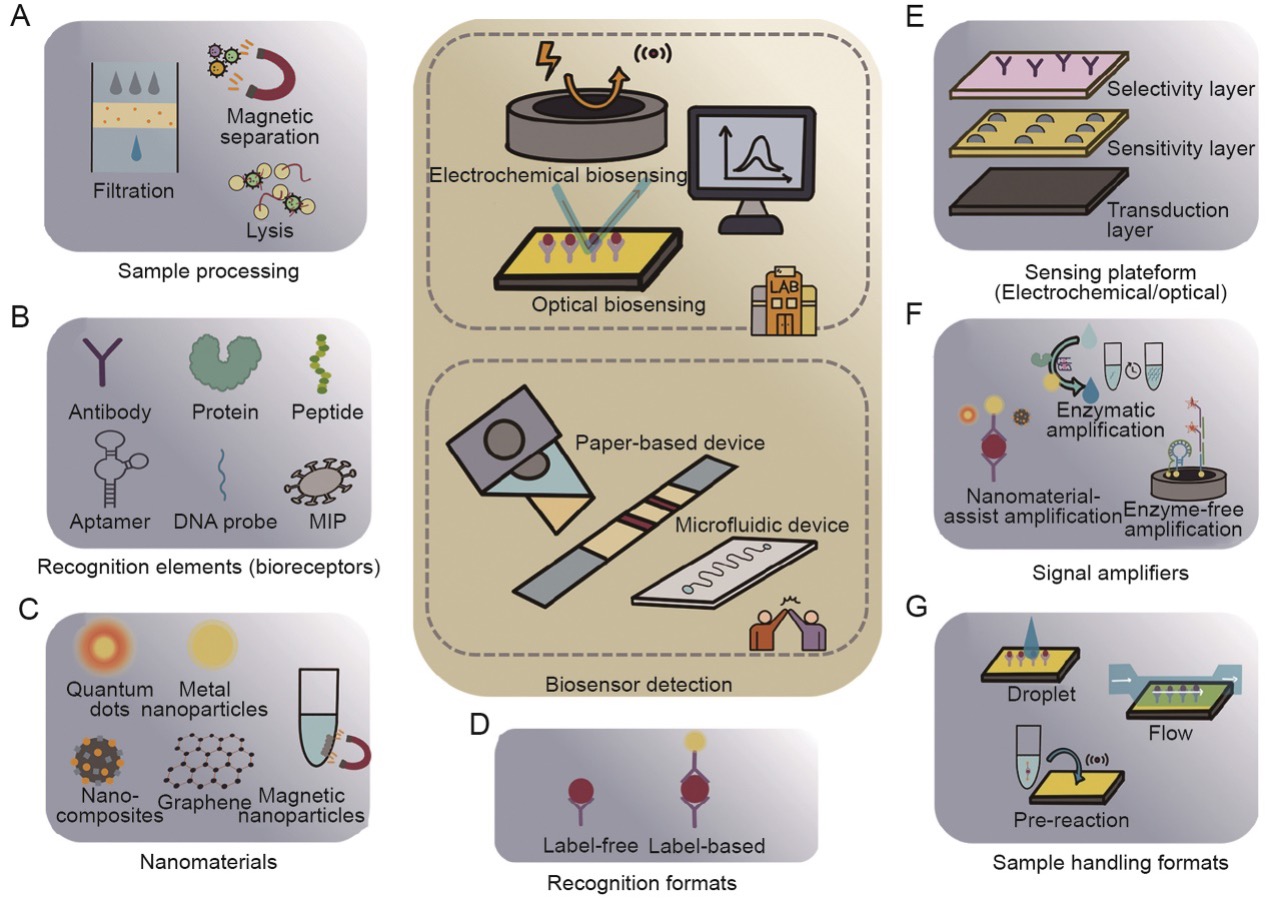
Fig. 2: Summary of the components involved in waterborne virus biosensing in wastewater. (A) Sample preprocessing to reduce interferents. (B) Target recognition elements with high specificity and stability. Selection of (C) nanomaterial types, (D) recognition formats, (E) sensing platform, (F) signal amplifying methods, and (G) corresponding sample handling formats.