近日,西湖大学先进神经芯片中心的三篇论文分别获学术顶会IEEE-CICC 2024及ICLR 2024收录。
其中,有两项成果被集成电路领域顶级会议IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC 2024)收录, 一项成果被深度学习领域顶会International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2024)收录,实现了本中心在集成电路领域和人工智能领域科研成果并蒂开花。
Recently, three papers from CenBRAIN Neurotech Center of Excellence were accepted at two top academic conferences, IEEE-CICC 2024 and ICLR 2024. Two contributions were selected for this IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC 2024), a top conference in the field of integrated circuits. One achievement was accepted by the top conference in the field of deep learning, the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2024). This highlights the research achievements of the center in both integrated circuits and artificial intelligence fields, showcasing its leading position in pioneering research within these pivotal fields.

IEEE定制集成电路会议(CICC)是集成电路设计领域世界顶级会议之一,以论文录用率低、研究成果创新性和实用性强著称。会议内容涉及模拟电路设计、生物医学、传感器、显示器和MEMS,数字和混合信号SoC/ASIC/SIP,嵌入式存储器件等方面,重点讨论如何解决集成电路设计问题的方法,以提高芯片各项性能指标。
The IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC) is one of the world's top conferences in the field of integrated circuit design, renowned for its low paper acceptance rate and the innovative and practical nature of research outcomes. Each conference covers a wide range of topics, including analog circuit design, biomedical applications, sensors, displays, MEMS, digital and mixed-signal SoC/ASIC/SIP, embedded memory devices, and more. It focuses on discussing methods to address issues in integrated circuit design, aiming to enhance various performance metrics of chips.
《神经元启发的 0.0032mm2-1.38μW/Ch 具有直接多路复用前端和事件驱动尖峰检测与传输功能的无线植入式脑机接口》
陈锦波*,吴辉*, Razieh Eskandari,刘星,林思宇,侯启明,田丰实,邹文俊,杨杰,Mohamad Sawan
J. Chen*, H. Wu*, R. Eskandari, X. Liu, S. Lin, Q. Hou, F. Tian, W. Zou, J. Yang and M. Sawan, “A Neuron-Inspired 0.0032mm2-1.38μW/Ch Wireless Implantable Neural Interface with Direct Multiplexing Front-End and Event-Driven Spike Detection and Transmission”, IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), April 2024.
植入式神经接口需要极低功耗和面积,海量多通道神经信号的传输进一步加剧了功耗挑战。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种受神经元启发的无线植入式神经接口,它具有直接多路复用前端和事件驱动尖峰检测与传输功能,每个记录通道的面积和功耗为0.0032mm2-1.38μW,无线传输数据量减少 500 倍以上。
Implantable neural interfaces require minimal power consumption and area. The transmission of extensive multi-channel neural signals further exacerbates the power challenge. To address these challenges, this paper presents a neuron-inspired wireless implantable neural interface with direct multiplexing front-end and event-driven spike detection and transmission, achieving 0.0032mm2-1.38μW per recording channel with more than 500x data reduction.
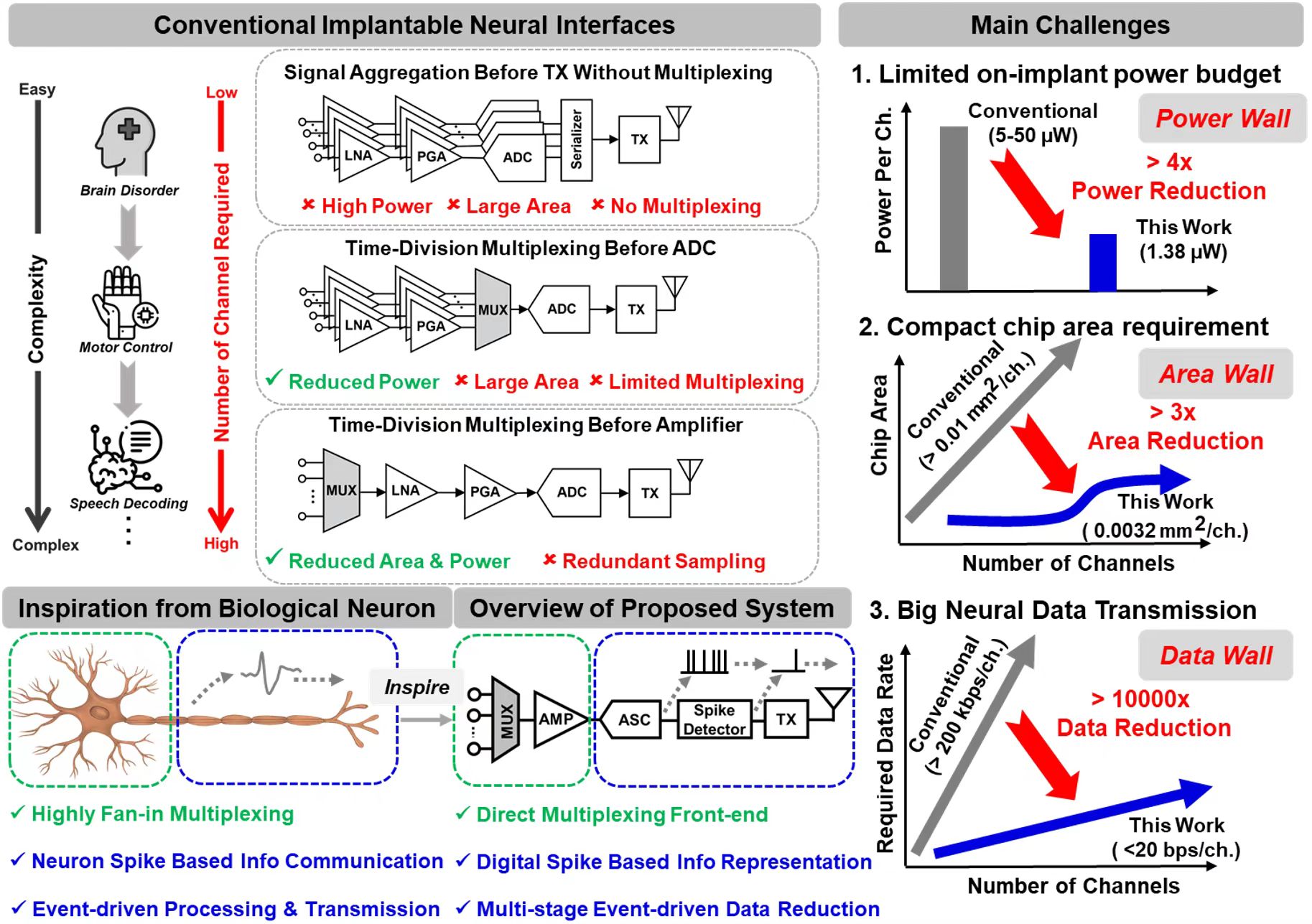
图 1. 传统植入式神经接口(上图)与主要挑战(右图),以及受生物神经元启发的本文提出系统概览(下图)
Fig. 1: Conventional implantable neural interfaces (top) with main challenges (top, right), and overview of proposed system inspired from biological neuron (bottom).
《一款0.078pJ/SOP的具备三维计算阵列与非结构化稀疏技术的脉冲注意力/卷积处理器设计》
方潮铭*,沈子扬,赵仕琪,王传庆,田丰实,杨杰,Mohamad Sawan
C. Fang*, Z. Shen, S. Zhao, C. Wang, F. Tian, J. Yang and M. Sawan, " A 0.078 pJ/SOP Unstructured Sparsity-Aware Spiking Attention/Convolution Processor with 3D Compute Array," IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), April 2024.
大规模的脉冲神经网络,如脉冲transformers,已经达到了与传统ANN相当的性能,但其计算成本要低得多。然而,SNN的能量效率在很大程度上取决于稀疏性,在网络稀疏率较低时,能效会有较大程度的下降。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了第一个非结构化稀疏性感知的脉冲注意力/卷积加速器。它采用3D阵列,最大限度地提高脉冲神经网络中不同时间步的数据复用率,以减少外部存储器访问。我们还设计了一种具有优先级编码器阵列的并行非零数据提取器来搜索和提取多个非零脉冲-权重对,以提高利用非结构化稀疏性的性能。本工作在台积电40nm制程下完成流片验证,与最先进的稀疏处理器相比,它实现了0.078pJ/SOP的最佳能效,利用脉冲transformers算法,实现了77.6%的ImageNet图像识别准确率。
Large-scale SNNs, such as spiking transformers, show comparable performance to ANNs but at a much lower computational cost. However, the energy efficiency of SNN depends heavily on sparsity and may deteriorate at low sparsity level. To solve this problem, we present the first unstructured-sparsity aware spiking attention and convolution accelerator. It features a 3D array to maximize data reuse across different timesteps in SNN to reduce external memory access. A parallel non-zero data fetcher with priority-encoder array is implemented to search and fetch multiple non-zero spike-weight pairs to boost the performance of exploiting unstructured sparsity. A unified scheduler is applied to achieve a balanced efficiency for multiple operators involved in spiking transformers. The accelerator is fabricated using 40nm technology and compared with state-of-the-art sparse processors, it achieves the best energy efficiency of 0.078pJ/SOP and a highest 77.6% recognition accuracy for ImageNet with the spiking transformer algorithm.
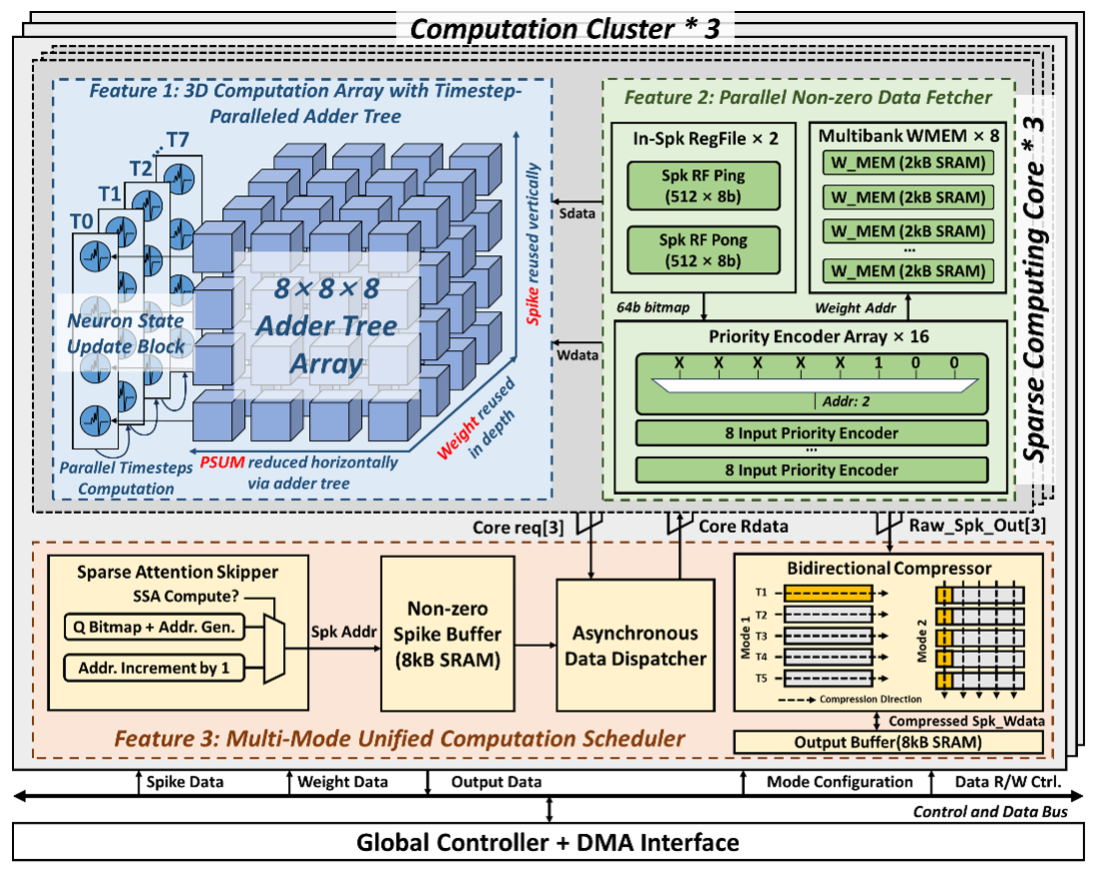
图1. 具有稀疏三维阵列技术的脉冲神经网络加速器整体架构图
Fig. 1: Overall architecture and key design features for the unstructured sparsity-aware SNN accelerator with 3D computation array.
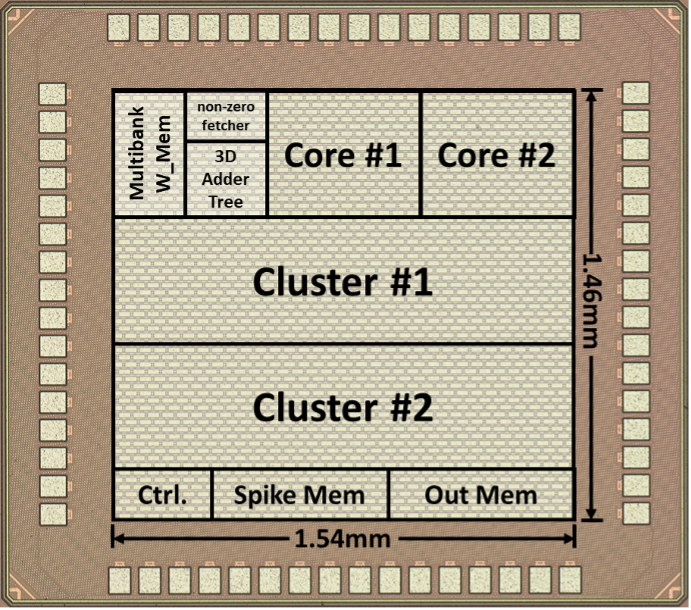
图2. 通过TSMC 40nm流片后的芯片显微图
Fig. 2: Chip micrograph under TSMC 40nm CMOS

International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)是国际公认的深度学习顶会之一。该会议展示和发布人工智能、统计学和数据科学领域使用的深度学习各个方面的前沿研究,以及机器视觉、计算生物学、语音识别、文本理解、游戏和机器人学等重要应用领域的前沿研究而享誉全球。
The International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) is internationally recognized as one of the premier conferences in the field of deep learning. It is globally renowned for presenting and publishing cutting-edge research on all aspects of deep learning used in the fields of artificial intelligence, statistics, and data science, as well as important application areas such as machine vision, computational biology, speech recognition, text understanding, gaming, and robotics.
《 一种适用于视网膜假体的刺激图案生成与验证算法》
王传庆*,吴迪*,方潮铭,杨杰,Mohamad Sawan
C. Wang*, D. Wu, C. Fang, J. Yang and M. Sawan, “Exploring Effective Stimulation Patterns via Vision System Modeling for Visual Prostheses,” International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), May 2024.
视网膜假体是帮助盲人恢复视力的设备,其性能在很大程度上取决于植入电极阵列的刺激图案质量。然而,现有的处理框架优先考虑如何生成刺激图案,而忽略了对于上述图案的有效验证,进而无法正确评估刺激图案的质量。在本文中,我们首次提出了一种端到端的刺激图案生成和验证框架(StimuSEE),它能利用 V1 神经元的脉冲响应信号作为监督,生成具有视力恢复效果的刺激图案。StimuSEE 由用于预测刺激图案的视网膜网络、光幻视仿真模型和初级视皮层网络(PVS-net)组成,其中PVS-net用于模拟从视网膜到视觉皮层的信号处理,并预测 V1 神经元的脉冲发放率。实验结果表明,预测的刺激图案与原始场景具有相似的特征,其不同的刺激幅值作用于正常细胞后,会激发相似的发放率。从数值上看,预测的发放率与记录的正常神经元反应的皮尔逊相关系数达到 0.78。
Visual prostheses are potential devices to restore vision for blind people, which highly depends on the quality of stimulation patterns of the implanted electrode array. However, existing processing frameworks prioritize the generation of stimulation while disregarding the potential impact of restoration effects and fail to assess the quality of the generated stimulation properly. In this paper, we propose for the first time an end-to-end visual prosthesis framework (StimuSEE) that generates stimulation patterns with proper quality verification using V1 neuron spike patterns as supervision. StimuSEE consists of a retinal network to predict the stimulation pattern, a phosphene model, and a primary vision system network (PVS-net) to simulate the signal processing from the retina to the visual cortex and predict the firing rate of V1 neurons. Experimental results show that the predicted stimulation shares similar patterns to the original scenes, whose different stimulus amplitudes contribute to a similar firing rate with normal cells. Numerically, the predicted firing rate and the recorded response of normal neurons achieve a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.78.
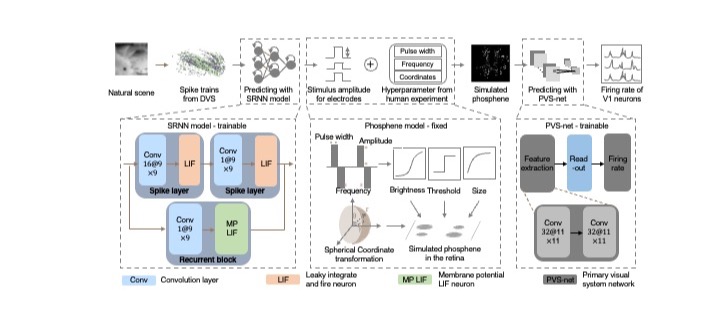
图1. 本文提出的StimuSEE端到端处理框架的技术细节
Fig. 1: The technology details of proposed end-to-end processing framework (StimuSEE).
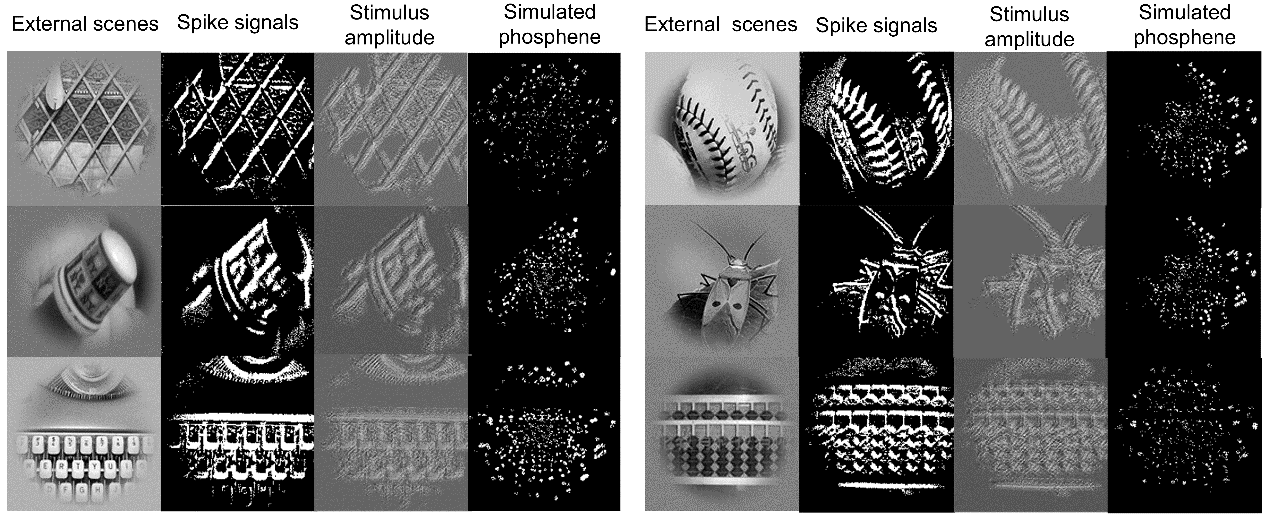
图2. StimuSEE的各个模块在处理过程中数据流的可视化
Fig. 2: Visualization of data flow after processing by different modules of StimuSEE.