The convergence of neuroscience and electronic engineering is driving neuroelectronic systems into a new era defined by intelligence and precision. Closed-loop neuromodulation (CLNM) is emerging as a pivotal focus in this field, facilitating adaptive interventions in abnormal neural activity through real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustments of stimulation parameters. This mechanism not only holds tremendous promise for treating a variety of neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, depression, and chronic pain, but also paves the way for new technological advancements in personalized neural therapy.
In recent years, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly enhanced the capabilities of closed-loop neuromodulation systems. AI-driven signal processing and adaptive control algorithms empower these systems to identify complex neural patterns, enabling more precise feedback control and improved responsiveness.
Figure 1. Basic concepts of seizure prediction systems: (a) Highly integrated seizure prediction system including a bio-interface or micro-electrode array to collect bio-signals such as EEG, ECoG, and an integrated circuit for analog and digital processing. (b) Key digital and analog hardware blocks to building a closed-loop neuromodulation (CLNM) system. (c) The goal of the system is to classify different seizure stages based on the captured bio-signals. (d) Performance of the system is characterized by various metrics such as receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), area under curve (AUC), which are determined by true positive rate (TPR) and false positive rate (FPR) of the system.
At the same time, rapid advancements in Integrated Circuit (IC) technology have established the hardware foundation for low-power, high-bandwidth, and highly integrated embedded neural interfaces. These innovations allow closed-loop systems to execute real-time computations and decision-making in miniaturized and low-latency environments. The synergistic fusion of AI and IC technologies is laying the groundwork for the realization of “on-chip intelligence for neuromodulation” in the future.
Despite significant progress in AI-driven and IC-supported closed-loop neuromodulation systems within academic research, translating these innovations into clinical practice remains challenging. Issues such as limited data generalizability, trade-offs between real-time performance and power consumption, long-term in vivo stability, and biocompatibility constraints continue to pose hurdles. Furthermore, the complexities of clinical environments necessitate increased algorithmic robustness, enhanced hardware safety, and a capacity for individualized parameter tuning. Thus, there is an urgent need to systematically review existing research, analyze the collaborative roles of AI and IC technologies in CLNM, and assess their clinical applicability.
In this context, a review paper led by Chair Professor Mohamad Sawan’s research center, recently published in the emerging journal Neuroelectronics, aims to deliver a clinically oriented systematic review of the latest advances in AI-driven closed-loop neuromodulation algorithms and IC-enabled neural interface technologies. This work evaluates their effectiveness, limitations, and evolving trends within clinical practice while proposing a forward-looking roadmap that integrates AI and IC innovations to meet unmet clinical needs. Designed to serve as a valuable resource, this review aims to advance the research and application of intelligent neuroelectronic systems.
Our Ph.D. candidate Junzhe Wang and Yunsheng Liao are the co-first authors, with Dr. Jie Yang and Prof. Mohamad Sawan as corresponding authors.
Research Highlights
1) Provide an overview of state-of-the-art AI-driven algorithms and IC-enabled technologies;
2) Summarize the CLNM landscape which emphasizes the clinical practice-oriented perspective;
3) Clarify the effectiveness of implementing CLNM in clinical settings;
4) Describe the roadmap for integrating AI and IC innovations to address unmet clinical needs.
Abstract
Closed-loop neuromodulation (CLNM) has emerged as a transformative approach for treating neurological disorders, enabling precise and adaptive interventions through real-time monitoring and modulation of neural activity. Although advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have unlocked new possibilities for more accurate closed-loop systems, and significant progress has been made in this area within academia, challenges persist in translating these technologies into clinical practice. Similarly, integrated circuits (IC) have been pivotal in optimizing power consumption, latency, and device miniaturization. However, further innovations are still required to meet the stringent demands of clinical environments. This review not only provides an overview of state-of-the-art AI-driven algorithms and IC-enabled technologies that are reshaping the neuromodulation landscape but also emphasizes a clinical practice-oriented perspective. Through analysis of related clinical trials, we highlight both the effectiveness and the obstacles of implementing these technologies in clinical settings. Finally, we propose a roadmap for integrating AI and IC innovations to address unmet clinical needs, offering insights into the future of CLNM.
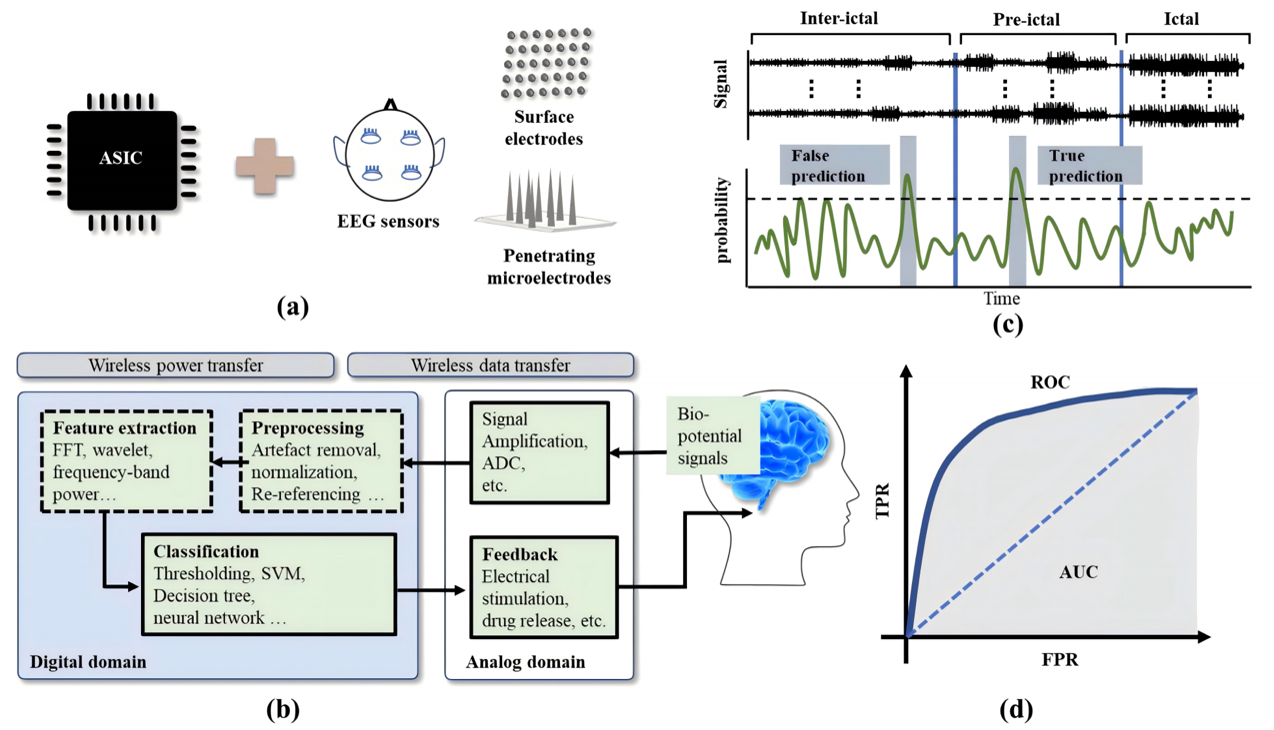
Fig 2. Building blocks of conventional biomedical devices. EEG, EMG, and ECG are among the biosignals used for various applications, including seizure prediction, arrhythmia detection, and gesture recognition.